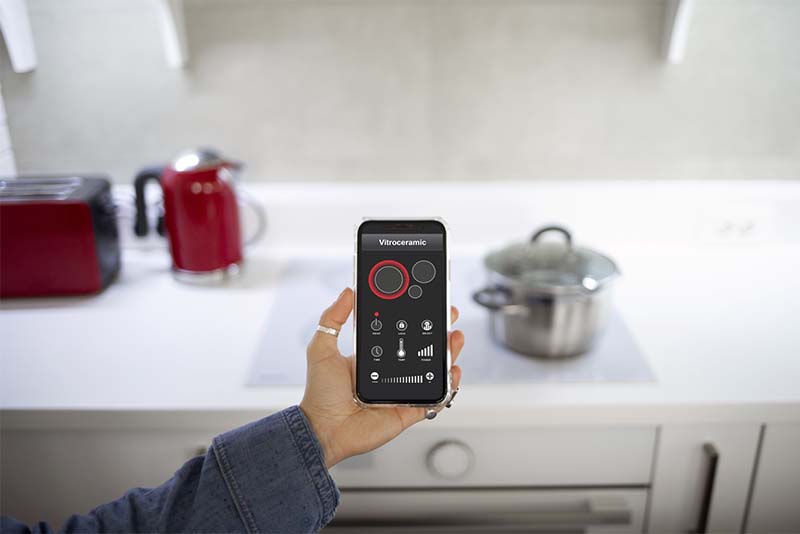
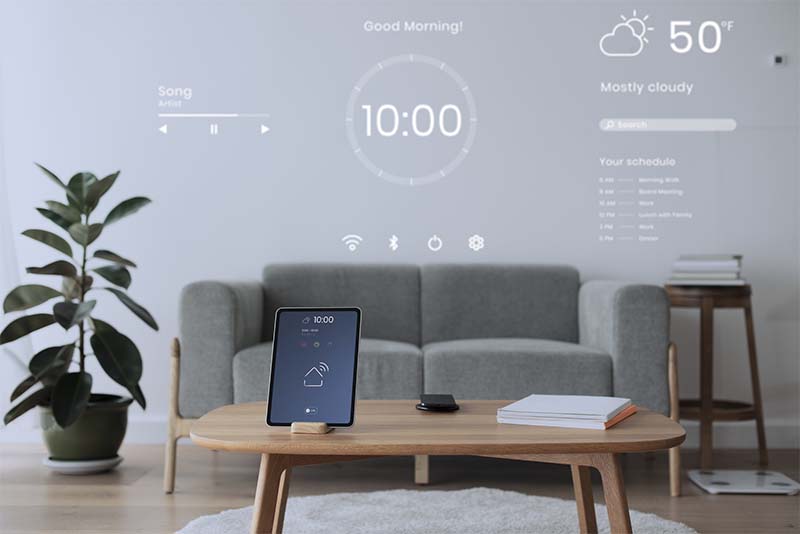
One of the main features of contemporary smart home energy monitors is real-time energy tracking, which enables homeowners to keep an eye on their electricity usage as it occurs. Real-time tracking offers constant insight into how and when energy is being used throughout the day, in contrast to traditional utility bills that only provide a monthly snapshot.
A smart energy monitor is connected to the home’s electrical panel or meter in order for this technology to function. After that, the gadget gathers comprehensive usage data, which is instantly sent to a web dashboard or companion app. Users get instant insight into their consumption patterns by seeing their current energy usage expressed in kilowatts (kW) and occasionally in dollars per hour.
Finding high-consumption appliances or habits is one of the main advantages of real-time tracking. For instance, the homeowner might want to think about switching to a more energy-efficient appliance or using alternate drying techniques if turning on the dryer results in a discernible increase in energy usage. When appliances like ovens or space heaters are accidentally left on, users can get real-time feedback so they can take quick action and reduce waste.
The possibility of changing behavior is an additional benefit. Users are more likely to adopt energy-saving behaviors when they can observe the direct results of their actions on energy use, such as how turning off lights or lowering air conditioner settings reduces consumption. This can eventually result in considerable financial savings and a lessened environmental effect.
Real-time energy consumption monitoring is essential for homes with time-of-use electricity rates. By monitoring your energy consumption as it happens, you can shift your usage to those less costly, off-peak hours, as these rates can rise during peak hours. Additionally, some systems even employ machine learning to identify specific patterns in the energy usage of different appliances, greatly increasing the accuracy of the data. Users can make well-informed decisions that lower energy costs and boost overall efficiency when this is combined with intelligent alerts.
In summary, real-time energy tracking empowers homeowners with actionable insights and immediate feedback, making energy management intuitive, efficient, and impactful.
- Appliance-Level Monitoring
Advanced smart home energy monitors have a feature called appliance-level monitoring that lets users keep tabs on how much electricity is being used by specific devices in their house. By determining how much power each appliance uses, this level of detail goes beyond whole-home monitoring and allows for more accurate cost and energy management control.
Appliance-level monitoring is implemented in two primary ways. The first is by using smart outlets or plugs, which are connected to particular appliances after being inserted into regular wall sockets. These gadgets record the amount of power used by anything connected to them and transmit the information to a dashboard or central app. Although this approach is easy to use and reasonably priced, each monitored appliance needs its own smart plug.
The second approach makes use of disaggregation or circuit-level technology, which is present in more sophisticated energy monitors. These systems use machine learning algorithms to determine each appliance’s distinct energy signature after connecting to the home’s electrical panel. A refrigerator’s on/off cycle, for example, differs from that of a washing machine or microwave. This configuration offers a smooth, automated monitoring experience without requiring additional hardware for every device.
Monitoring at the appliance level has many advantages. It first aids in identifying energy hogs, or gadgets that use a lot of electricity, particularly those that are outdated or inefficient. Homeowners are able to make well-informed choices regarding the replacement or reduction of such appliances. Secondly, it makes it possible to identify broken equipment. A malfunctioning appliance that uses more electricity than usual could result in increased expenses or even safety risks.
Better budgeting and energy-saving techniques are also supported by this feature. Users can modify usage patterns or program shutdowns during periods of high energy costs by knowing which appliances are the biggest contributors to their bills. Additionally, it promotes responsible energy use and increased awareness.
In conclusion, appliance-level monitoring brings transparency to household electricity usage, enabling smarter decisions, improved efficiency, and cost savings. It transforms abstract energy data into clear, actionable insights that empower users to take control of their energy footprint.
One important function of smart home energy monitors is cost estimation, which converts raw data on energy use into a clear picture of the homeowner’s electricity usage costs. Cost estimation tools use this information in conjunction with local utility rates to determine current and anticipated electricity costs, rather than just displaying energy use in kWh.
The ability of the energy monitor to track power consumption throughout the day is central to cost estimation. The cost is then calculated by multiplying this data by the homeowner’s utility rate, which may be a variable time-of-use (TOU) pricing model or a flat rate. While some smart monitors can automatically sync with nearby utility providers for precise, real-time pricing, many others let users manually enter their electricity rate.
For instance, the cost estimation tool will display $0.30 for a device using 1.5 kWh over two hours if the local electricity rate is $0.20 per kWh. In order to give homeowners a financial picture of their energy usage, the monitor gradually incorporates these micro-costs into daily, weekly, and monthly summaries.
Cost estimation is especially useful for households with TOU plans, where demand drives electricity prices. With real-time cost tracking, users can significantly lower their bills by relocating their consumption to off-peak hours and avoiding times of high usage.
Forecasting the budget is yet another important benefit. By looking at historical data and consumption trends, many smart monitors can predict monthly electricity bills. This helps households avoid unexpected expenses and create a budget. Some systems even set budget alerts to alert users when their consumption is about to exceed a predefined financial threshold.
Moreover, appliance-level cost breakdowns can reveal which gadgets consume the most energy. Insightful actions like unplugging unused electronics, switching to energy-efficient appliances, or using less during peak hours are encouraged by this realization.
In summary, cost estimation turns abstract energy data into practical financial insights. It empowers homeowners to make cost-effective choices, avoid surprises on their bills, and actively manage their energy budget in a smarter, more sustainable way.
Mobile app integration is one of the most practical and important features of modern smart home energy monitors. These specialized mobile applications serve as the primary hub for real-time access, interpretation, and action on energy data from a smartphone or tablet. Energy management is made easier, more transparent, and more controlled by this feature.
Users can view historical usage trends, cost estimates, and real-time energy consumption from any location once the smart energy monitor is installed and connected to the app. With dashboards, graphs, and color-coded indicators that make complex energy data easier to understand, the interface is usually made to be user-friendly. Customers can now understand their power usage without having to see the actual device or rely just on their monthly bills.
Remote monitoring and control is a key benefit of integrating mobile apps. Homeowners can monitor their energy use while they’re away from home, get real-time notifications about odd power consumption spikes, or find out if an appliance was inadvertently left on. In order to save energy, some apps even integrate with smart thermostats or plugs, allowing users to remotely turn devices on or off.
The majority of mobile applications also offer customizable notifications. Customers may receive notifications when certain devices are using more power than usual, when peak charges apply, or when power usage surpasses a predetermined threshold. Active notification encourages prompt action and avoids bill shock.
Users can log in on multiple devices or even share access with family members using mobile apps, which are an excellent way to access your accounts from multiple devices. Additionally, a lot of these apps use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to provide detailed reports, energy-saving advice, and customized insights based on your usage.
Integration with voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, or Apple Siri is another feature commonly available through mobile apps, offering hands-free control and updates through simple voice commands.
In conclusion, mobile app integration transforms a smart energy monitor from a passive tracking device into an interactive, intelligent energy management tool. It provides convenience, real-time feedback, and control—empowering users to make informed decisions and build sustainable habits that reduce both energy consumption and costs.
The ability of smart home energy monitors to send alerts about energy usage is one of their best features. When unusual or excessive electricity consumption occurs, these alerts promptly notify homeowners. These alerts are primarily intended to assist individuals in monitoring their energy usage more closely, reducing waste, spotting possible issues early, and eventually lowering their utility costs.
Data on household electricity consumption, frequently down to individual appliances, is continuously gathered by smart energy monitors. They instantly send out alerts through a push notification, email, or mobile app when they notice an abrupt spike, an odd pattern, or energy consumption that surpasses a predetermined threshold. This makes it possible for users to promptly take corrective action, such as shutting off an overlooked appliance or looking for broken equipment.
An energy usage alert, for instance, can alert the homeowner before a significant amount of energy is wasted if a space heater is inadvertently left on while no one is home. In a similar vein, the system can identify an abnormality if a refrigerator starts using more power than usual because of a malfunctioning compressor, enabling maintenance before the appliance completely fails.
Households with time-of-use (TOU) electricity plans will find these alerts particularly helpful. Reminders can be sent to users to switch to less expensive, off-peak hours and use less energy during peak hours when rates are highest.
Alerts about energy use are frequently customizable. Homeowners can establish consumption limits for individual appliances or the entire house, and they will be notified when those limits are exceeded. Users of certain systems can even set up daily, weekly, or monthly energy budgets and receive alerts if their usage exceeds predetermined thresholds.
Alerts can also encourage energy-efficient behavior. Users are urged to adopt more intelligent practices, like unplugging devices when not in use or turning off lights in vacant rooms, by demonstrating the instantaneous effects of energy decisions.
In summary, energy usage alerts turn passive energy data into proactive tools for energy management. They provide real-time insights, promote efficiency, and help homeowners stay in control of their electricity usage, making smart home energy monitoring more dynamic, responsive, and impactful.
Historical analysis of data, through which users can see and analyze their past energy consumption across several time frames, such as day, week, month, and even year, is an important aspect of smart home energy monitoring devices. Inefficiencies are identified, trends are understood, and informed energy decisions are made by homeowners through such analysis of raw usage data turned into valuable information.
Energy monitors can show consumption trends through timelines, graphs, and charts by storing and organizing data on electricity usage over time. Users can quickly compare energy use over various time periods, such as weekdays versus weekends, summer versus winter, or month-to-month, with the aid of these visualizations. This comparison is useful for identifying seasonal spikes or recurrent patterns that might be missed without long-term monitoring.
For example, the homeowner will be aware that their winter usage is significantly greater due to heating, or that holiday-related appliances are higher in energy usage. They can use this information in informing better plans, for example, changing thermostat, scheduling maintenance, or replacing less efficient appliances.
Goal-setting and progress monitoring also heavily rely on the analysis of historical data. Users can set monthly usage or cost targets with a lot of energy monitors. By comparing current usage to past months, the historical data serves as a benchmark. This enables users to see whether their actions—like shutting off unused electronics or using appliances during off-peak hours—are truly having an impact.
Historical data analysis can also be applied to track the generation and use of energy over time in houses that have solar panels installed. It allows users to calculate whether they are relying more on solar or grid electricity during various periods throughout a year, as well as to understand their return on investment.
Moreover, the information can be exported and shared for additional analysis, whether for utility company reporting, energy audits, or individual budgets.
In conclusion, historical data analysis empowers homeowners with long-term visibility into their energy habits. It turns past usage into actionable knowledge, supports smarter energy planning, and helps reduce waste, costs, and environmental impact. It’s an essential tool for anyone looking to optimize their home’s energy efficiency over time.
Ease of compatibility with other smart platforms and devices, e.g., Apple HomeKit, Google Assistant, Amazon Alexa, and smart thermostats, is an important aspect of modern energy monitors. Such integration enhances user experience through interactive, automated, and voice-activated energy monitoring.
Users can incorporate usage data into larger smart home routines or use voice commands to access energy insights when a smart energy monitor is compatible with home automation platforms. For instance, a user can ask Alexa or Google Assistant, “How much electricity did I use today?” or “What’s my current energy cost?” and receive immediate, spoken responses.
In addition to voice communication, energy monitors can collaborate with other gadgets thanks to smart home compatibility. For example, the system can automatically dim smart lighting, turn off smart plugs, or adjust smart thermostats to save energy if consumption reaches a predetermined threshold. Without the need for human intervention, these automations contribute to a reduction in energy waste.
It is particularly advantageous to integrate with smart thermostats such as Nest or Ecobee. In order to increase heating and cooling efficiency based on occupancy patterns and electricity rates, the thermostat can exchange usage data with the energy monitor. More intelligent temperature adjustments and energy savings result from this dynamic response to real-time data.
Additionally, users can create custom rules if the system is compatible with IFTTT (If This Then That) or other automation tools. For instance: “Send me a text if energy usage exceeds 3 kW,” or “Switch off non-essential appliances when I leave the house.” A customized and effective home energy environment is produced by these clever routines.
Additionally, some systems support central hubs or smart home dashboards, which let users manage several elements of their house, such as energy, lighting, and climate, from a single app or interface. Convenience and user engagement are enhanced by this centralized control.
In conclusion, energy monitors are much more than stand-alone gadgets when they are compatible with smart homes. As they integrate with other smart technologies, they become a crucial component of a fully connected home, providing users with automation, convenience, and improved control to help them live more sustainably and use less energy.
- Carbon Footprint Insights
An increasingly useful feature of smart home energy monitors is carbon footprint insights, which are intended to assist users in comprehending how their electricity use affects the environment. Energy monitors with carbon tracking capabilities go one step further by converting energy use into carbon emissions, which are typically measured in kilograms or pounds of CO₂. Traditional energy monitors only consider usage and cost.
This feature integrates historical or current energy usage data with regional carbon intensity metrics. These metrics indicate how clean or dirty the local electrical grid is, depending on the power generation sources (e.g., coal, natural gas, solar, wind). For example, using one kWh of electricity in a coal-powered region results in higher CO₂ emissions than using the same amount of electricity in a renewable energy-powered region.
Smart energy monitors provide a more tangible representation of the invisible environmental cost of electricity by displaying this data in an easy-to-use dashboard. Users can see how specific behaviors, such as using high-energy appliances during peak hours or running the air conditioner all day, affect their carbon footprint and view daily, weekly, or monthly carbon emissions.
Aside from creating awareness, these discoveries give power to the users to meaningfully act upon it. For instance, they can opt for more efficient devices, cut back on non-essential usage, or use appliances at times when the grid is cleaner. Some systems even recommend specific activities to lower emissions, like washing clothes in cold or switching to LED lighting.
Monitoring one’s carbon footprint can also encourage the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels. By allowing users to directly compare their emissions before and after making the switch to solar power, clean energy investments are shown to be worthwhile.
In summary, carbon footprint insights bridge the gap between personal energy consumption and global environmental impact. By making emissions data accessible and actionable, smart home energy monitors help users live more sustainably, reduce their environmental footprint, and make energy choices that align with climate-conscious values.
A specialized feature of some sophisticated smart home energy monitors made for homes with solar photovoltaic (PV) systems is solar power monitoring. This feature helps homeowners get the most out of their solar investment by giving them comprehensive information about how much energy is being produced, used, and exported to the grid.
A solar power monitoring system, which frequently connects directly to the solar inverter or meter, tracks the electricity produced by the solar panels in real time. Users can clearly see how much solar power is used locally versus how much is taken from the grid thanks to the data it shows alongside household energy usage.
Optimizing self-consumption is one of the main benefits. Homeowners can plan energy-intensive tasks like running dishwashers, washing machines, or EV charging during periods of high solar generation by precisely timing when their solar panels are generating electricity. This lowers energy costs and dependence on the grid.
Another benefit of solar monitoring is the ability to track surplus energy export, or the quantity of solar power that is returned to the grid. When net metering or feed-in tariffs are in place, this exported power frequently converts into credits or payments; keeping an eye on it guarantees homeowners fully comprehend their financial returns.
Users can also receive performance alerts from the system in the event that unexpected drops in solar generation occur as a result of equipment problems, dirt on panels, or shading. Early identification of these issues preserves system performance and safeguards the solar investment.
Long-term analysis is further supported by solar power monitoring, which displays production trends in relation to weather, seasons, and system age. Schedules for maintenance and system upgrades can be informed by this data.
Some smart monitors provide a thorough picture of overall energy flow and savings by combining solar data with estimates of grid consumption and costs. User convenience and control are further improved by integration with smartphone apps and smart home platforms.
In conclusion, by offering clear, real-time insights into production and usage, solar power monitoring enables homeowners to get the most out of their solar systems. Better energy decisions, more savings, and greater environmental benefits result from this.
- Energy Saving Recommendations
Energy-saving suggestions are a useful function of smart home energy monitors that assist users in lowering their electricity usage by providing tailored advice and practical suggestions based on historical and real-time energy data. These suggestions go beyond simple consumption data and convert them into doable actions that homeowners can take to increase productivity, cut costs, and lessen their environmental effect.
In order to pinpoint areas where energy is being wasted or could be optimized, smart energy monitors examine usage trends, appliance efficiency, and periods of peak demand. For instance, the monitor may suggest switching to a more energy-efficient refrigerator if it notices that an old model frequently uses a lot of power. In a similar vein, the system might recommend using smart lighting controls or switching to LED bulbs if lighting consumes a significant amount of electricity.
Numerous systems employ machine learning or artificial intelligence algorithms to gradually improve suggestions, customizing them to each household’s particular appliances and habits. This personalization improves the suggestions’ efficacy and relevance, facilitating users’ ability to take significant action.
Behavioral advice is frequently included with recommendations. Users may be advised, for example, to use washing machines or dishwashers during off-peak hours to benefit from lower energy rates or to use fewer high-demand appliances at once to prevent peak surcharges. Device unplugging when not in use may be encouraged by alerts regarding standby power consumption..
In addition to individual homes, some smart monitors incorporate weather forecasts or community data to recommend the best times to use energy or alert users to anticipated spikes in grid demand. This more comprehensive viewpoint promotes grid stability and facilitates user participation in demand response initiatives.
These suggestions are usually provided by mobile apps in the form of clear dashboards, alerts, and reports; occasionally, challenges or objectives are used to gamify energy conservation. Long-term energy-conscious habits are fostered by this engagement.
Overall, energy conservation recommendations convert information into usable knowledge. Besides lowering the costs and ease of living sustainably, they allow homeowners to make informed choices, increase appliance efficiency, and adjust daily routines, all of which pay off in terms of costs and carbon footprints saved.