Without using conventional keys, users can now enter restricted areas thanks to keyless entry, a contemporary convenience and security feature. Keyless entry systems, which are frequently found in homes, automobiles, and commercial buildings, use a variety of electronic techniques, including keypads, Bluetooth, RFID, biometrics, and smartphone apps. Compared to traditional keyed locks, this technology has a number of benefits. It lowers the possibility of losing or stealing physical keys by doing away with the necessity to carry them. Users can unlock doors more quickly and easily by tapping their phone or entering a passcode using an app or keypad.Keyless entry adds convenience and security to cars by allowing doors to unlock automatically when the authorised key fob is in close proximity. Keyless entry systems can be connected to voice assistants or automation tools in smart homes, giving users the ability to remotely control entry or create personalised access schedules for family members, visitors, or housekeepers. Furthermore, logging features that record who entered and when are frequently included with keyless entry systems. These features can be helpful for keeping an eye on access in both residential and commercial settings. Visitors can also be given temporary or one-time codes, which eliminates the need to give out extra keys. Although keyless entry has many advantages, there are drawbacks as well. Technical issues, power outages, and hacking can all affect electronic systems. Consequently, trustworthy.To avoid lockouts, some systems additionally incorporate emergency power options or physical key overrides. As more people value convenience and smart technology in their daily lives, keyless entry is becoming more and more popular despite these reservations. As security technology develops, keyless entry will probably become even more difficult due to multi-factor authentication techniques like biometrics, geofencing, or AI-based recognition systems. All things considered, keyless entry is a noteworthy advancement in contemporary security that blends creativity and usefulness to satisfy the needs of a connected, fast-paced world.
Users can manage systems, access files, and complete tasks just as they would if they were physically present at a computer, network, or device when they connect remotely. We call this ability remote access. In today’s digital world, smart technology, remote work, and international collaboration have all gained importance. By enabling employees to access office systems from home or while on the go, remote access is a common tool used by businesses to boost flexibility and productivity. IT professionals can update software, do maintenance, and troubleshoot issues without being physically present by using remote access tools. For home automation outside of the office, remote access is crucial. Users can control home appliances such as smart. This offers not only convenience but also peace of mind—homeowners can check surveillance footage, adjust settings, or lock doors remotely, ensuring safety and energy efficiency. In the medical field, remote access supports telehealth services, allowing healthcare providers to consult with patients and access medical records securely from various locations. Education has also benefited, as students and teachers can interact through virtual learning platforms regardless of geographical barriers. However, while remote access offers many advantages, it also introduces security challenges. Unauthorized access, data breaches, and hacking are potential risks, especially if secure protocols are not followed. To mitigate these threats, organizations and individuals must use encryption, firewalls, strong passwords, and multi-factor authentication. VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) are commonly employed to establish secure remote connections over public networks. Real-time collaboration and global data access are made possible by increasingly sophisticated and user-friendly remote access as technology develops. Working from a coffee shop, controlling a smart home from overseas, or accessing important files in an emergency are just a few examples of how remote access has revolutionised our interactions with the digital world. It provides unmatched convenience and flexibility while highlighting the significance of cybersecurity.
- Integration with Smart Home Systems
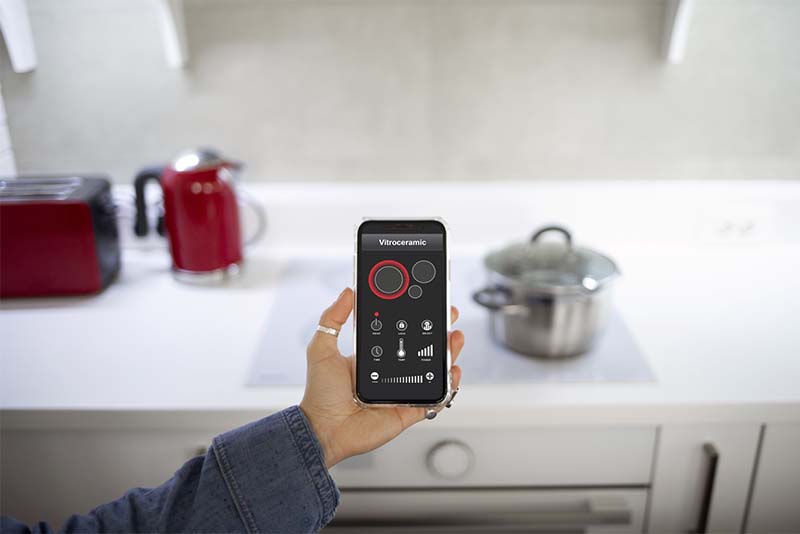
The smooth synchronisation and connection of multiple smart devices within a home to create a cohesive, automated, and practical living space is referred to as integration with smart home systems. Smart locks, lights, thermostats, security cameras, speakers, and appliances can all be controlled from a single platform thanks to this integration. Voice assistants and smartphone apps like Apple Siri, Amazon Alexa, and Google Assistant are frequently used to control these gadgets. Enhancing the user experience, enhancing security, increasing energy efficiency, and granting users greater control over household chores are the main objectives.When a user leaves the house, for instance, they can program the thermostat to change, the lights to turn off, and the doors to lock—all of which are controlled by a single command or geolocation detection. Voice control is also supported by integration, enabling hands-free task management—a feature that is especially useful for busy households or people with mobility issues. Homeowners can monitor and manage their property from any location in the world thanks to interconnected systems that offer remote access and real-time notifications. A proactive security environment can be created by using a security camera to detect motion. This allows the lights to turn on automatically and send a notification to the homeowner’s phone.Integration reduces utility costs and their detrimental environmental effects while improving energy management by adjusting lighting and heating based on occupancy and time of day. Despite all of the benefits, integrating smart home systems can be challenging due to privacy concerns, device compatibility issues, and the need for strong cybersecurity protocols. All devices need to support the same communication protocols, like Wi-Fi, Z-Wave, or Zigbee, in order to function seamlessly. In order to safeguard networks and stop unauthorised access to personal data, strong passwords and encryption are also crucial. With machine learning and artificial intelligence enabling predictive automation and personalised user experiences, integration is expected to become even more intelligent and intuitive as smart home technology advances. Overall, integrating smart devices into a centralized system transforms a traditional home into a dynamic, responsive environment that offers comfort, security, and efficiency.
Temporary access, especially in digital security and smart lock systems, is the ability to give people restricted access or permissions for a predetermined amount of time or for a specific purpose. In order to improve convenience and keep control over who can access a space and when, this feature is frequently utilised in both residential and commercial settings. For instance, homeowners can grant a visitor, housekeeper, or delivery person a temporary access code that will allow them to enter the house for a predetermined amount of time without having to give them a physical key.After the time limit has elapsed, the code is deemed invalid to guarantee that access is limited to the specified period. During business hours, contractors, maintenance staff, and part-timers are permitted temporary access to specific areas but not full access. By decreasing the possibility of unauthorised access and assisting in the tracking of who entered a space and when, this technique improves security. Mobile applications, cloud platforms, or centralised control systems that enable users or administrators to swiftly create, modify, and revoke permissions are frequently used to manage temporary access.Giving someone temporary login credentials so they can use software, access documents, or connect to a network is an example of temporary access that is not limited to physical locations. This feature is very helpful, but it needs to be used carefully. To avoid abuse, temporary codes or credentials should be safeguarded using authentication procedures and encryption. Activity logs and notifications, which notify owners or managers when someone uses their designated access, further improve transparency. In the age of the sharing economy, temporary access is also becoming more and more significant. For example, Airbnb hosts can boost productivity and improve the guest experience by providing short-term access to rental homes without the need for in-person meetings. In the end, transient As smart technologies continue to evolve, this feature is likely to become even more advanced, with customizable rules, biometric authentication, and real-time tracking playing a bigger role in how we control and share access.
Activity logs give a chronological account of events that take place over time and are comprehensive records of all actions carried out within a system, device, or network. Activity logs are essential for tracking usage, improving security, and preserving transparency when it comes to smart home appliances, security systems, and online platforms. Activity logs in smart locks or access control systems, for instance, can reveal who entered or exited a building, when they did so, and how they did it—by biometric scan, smartphone app, or keypad code. In places like homes, workplaces, and shared properties where several people may have access, this information is extremely helpful.Activity logs aid in determining the time and place of an incident in the event of a security breach or unauthorised entry, allowing for quicker and more precise reactions. Activity logs are used by IT systems in business settings to monitor user behaviour, system modifications, login attempts, and data access in order to support compliance with legal and security requirements. Because these logs enable administrators to track errors, keep an eye on performance, and identify questionable activity, they are also helpful for auditing and troubleshooting. Modern smart systems often store activity logs in the cloud, making them accessible through mobile apps or web dashboards, and sometimes integrating them with alerts or real-time notifications. This allows users to review recent actions and stay informed about the status of their devices or accounts. For example, if a smart lock is used during unusual hours, the system can flag the event and alert the homeowner. However, with the collection of such detailed data comes the responsibility of maintaining privacy and protecting sensitive information. Proper encryption, access controls, and data retention policies are essential to prevent misuse or breaches. As technology develops, activity logs become more complicated, with tools like predictive analytics and AI-driven pattern recognition helping users spot trends and take preventative action. Lastly, by providing an essential layer of accountability and insight in both personal and professional contexts, activity logs assist users in maintaining control, ensuring security, and optimising their systems.
- Enhanced Security Features
Modern tools and technologies known as enhanced security features are intended to give digital systems, physical locations, and personal information a higher degree of protection. These features provide more reliable, intelligent, and adaptable protection than conventional techniques like keys or passwords in the context of smart devices and contemporary security systems. Two-factor authentication (2FA), biometric authentication (such as fingerprint or facial recognition), and automatic lock timers that begin when the door is left unlocked for a predetermined amount of time are a few examples of features that smart locks can have. These improvements lessen the possibility of both human error and unauthorised access. Furthermore, many modern systems provide real-time alerts and notifications, which quickly inform users of unusual activity, such as an unsuccessful login attempt or unexpected access at strange hours. Surveillance systems can use motion sensors, night vision, and AI-powered facial recognition to identify people and identify suspicious activity. These days, certain security platforms use machine learning algorithms to learn user patterns and spot anomalies that could point to a threat. Encryption and secure cloud storage are two more crucial enhanced security features that prevent data from being intercepted or compromised during transmission and storage. In business environments, features like role-based access control (RBAC) ensure that users only have access to the information and tools necessary for their responsibilities, minimizing exposure of sensitive data. Additionally, security audits, automatic software updates, and tamper alerts are built into many systems to ensure that vulnerabilities are patched and unauthorized tampering is quickly identified. For personal devices and homes, geofencing can be used to trigger security actions based on a user’s location—for example, locking the doors when the homeowner leaves a defined area.These innovative features give users peace of mind and deter potential intruders by offering proactive, intelligent responses to threats. As physical security threats and cyber threats continue to evolve, the development and deployment of enhanced security features will remain essential for protecting people and their digital lives. Better security features offer a robust layer of protection in homes, workplaces, and online platforms in a world that is becoming more interconnected by the day.
Security technologies that employ distinct physiological or behavioural traits to confirm an individual’s identity are referred to as biometric options. These techniques are becoming more and more common in smart devices, access control systems, and digital authentication because they provide a very safe and practical substitute for conventional passwords, PINs, or physical keys. Voice recognition, iris scanning, fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, and even behavioural biometrics like typing patterns or gait analysis are examples of common biometric choices.Many smartphones, laptops, and smart locks use fingerprint scanning, one of the most popular biometric techniques. Access can be granted or denied based on its ability to identify the distinct ridge and valley patterns on a person’s fingertip. In order to improve accuracy and thwart attempts at spoofing using images or masks, facial recognition technology frequently uses infrared sensors or 3D mapping to analyse facial features and dimensions. Government and high-security settings commonly use iris scanning, a highly accurate technique that looks at the complex patterns in the coloured portion of the eye.Voice recognition uses speech patterns and speech characteristics to authenticate users. It is commonly integrated into virtual assistants and phone-based security systems. By concentrating on unique habits such as a person’s typing, swiping, or walking patterns, behavioural biometrics offer ongoing verification without compromising the user experience. Biometric options are hard to forget, share, or steal because they depend on something that is intrinsic to the user. One of their key benefits is this. This significantly reduces the likelihood of passwords and keys being misplaced or stolen. However, biometric systems also face challenges such as privacy concerns, data protection, and the potential for false positives or negatives. To avoid identity theft or unauthorised access, it is essential to make sure that biometric data is safely encrypted and stored. Furthermore, some people might find it uncomfortable to collect biometric data, or they might have medical conditions that make accuracy challenging. Despite these obstacles, biometric solutions are developing quickly and finding their way into more and more commonplace gadgets, such as office security systems, smart home locks, banking apps, and smartphones. In a digital world where convenience and safety are becoming more and more important, biometrics are an essential component of emerging authentication technologies due to their security, speed, and ease of use.
Battery-powered gadgets have become a vital part of modern technology because of their adaptability, portability, and simplicity of use in a variety of applications. Electronics, security systems, and smart home systems can operate without fixed power sources thanks to battery power, which makes installation easier and permits use in locations without direct access to electricity. Many wireless cameras, sensors, and smart locks, for example, are battery-operated, eliminating the need for complex wiring and reducing installation expenses. Battery-operated devices are particularly useful in emergency situations, such as power outages, because they ensure that security systems are operational when they are most needed. Most smart devices use rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, which provide long-lasting power and can be conveniently recharged without frequent replacements. Additionally, these devices often come with battery monitoring features that alert users when the battery level is low, helping to avoid unexpected downtime or lockouts. Efficient battery management is critical for the usability of such products, and manufacturers continually work to optimize power consumption to extend battery life. In order to minimise battery drain during periods of inactivity or low use, certain smart devices feature energy-saving modes or adaptive usage patterns. Devices that run on batteries have drawbacks despite their benefits. When batteries need to be changed or recharged, it can be inconvenient, especially if the device is in a difficult-to-reach place. Extreme temperatures can also impact battery performance and shorten battery life. Backup power solutions like external battery packs or manual overrides are frequently advised for crucial security applications in order to guarantee continuous operation. Battery-powered devices are perfect for both temporary setups and permanent installations due to their independence and convenience.As battery technology advances, we can expect smarter, more energy-efficient devices with longer operational lifespans and faster charging capabilities. Overall, battery-powered technology empowers users to implement flexible, reliable solutions in homes and businesses, contributing significantly to the growth of the smart device ecosystem.
When regular access methods fail, emergency access refers to the necessary features and provisions designed to ensure access to a device or secured area. In smart home security and access control systems, emergency access is an essential backup plan that prevents users from being locked out in the case of a power outage, device malfunction, or forgotten login information. For example, a physical key override feature on many smart locks allows homeowners to manually unlock the door in the event that the electronic system fails or the battery runs out. This physical key option ensures that access is never totally dependent on technology by providing a simple and reliable fail-safe.Additionally, some smart locks and security systems feature external power ports that let users temporarily recharge the device using a portable battery or power bank to get it back up and running in an emergency. Emergency access is also crucial in commercial and medical settings where timely entry may be required for safety or compliance. For firefighters, paramedics, or other authorised personnel to swiftly enter a building in an emergency, emergency override codes or master keys might be required. In order to balance convenience and security, emergency access methods are often closely monitored and controlled to prevent misuse or unauthorised entry.Certain systems provide controlled access while preserving security integrity by generating temporary emergency codes that are only valid for a brief period of time before being automatically deactivated. Emergency access on digital platforms can include account recovery tools like backup codes, trusted contacts, or biometric overrides that enable users to take back control of compromised or locked accounts. It takes careful planning to create emergency access features that are both user-friendly under pressure and impenetrable by intruders. Education and awareness are also essential because users need to understand when and how to use emergency access features. All things considered, emergency access is a crucial component of any security system that balances accessibility and protection to guard against malfunctions and lockouts. Because of technological advancements, emergency access solutions are always evolving to include safer and more intelligent options to help users navigate unexpected situations safely and effectively.
- Installation and Compatibility
Particularly when it comes to smart home technology and security systems, installation and compatibility are two important factors that affect how simple and effective smart devices are. While compatibility refers to how well a device integrates with current hardware, software, and smart home ecosystems, installation refers to the process of configuring a device to operate as intended. When buying smart locks, cameras, thermostats, or lighting systems, many users place a high value on an easy installation process.Generally speaking, devices that require little in the way of tools, wiring, or expert help are favoured because they enable homeowners to make quick and economical improvements to their homes. For instance, a lot of smart locks have adjustable parts to support various latch configurations and are made to fit standard door sizes and types. Because of this adaptability, users can install these devices more easily without having to significantly alter their doors. Since a device’s functionality frequently depends on its capacity to communicate with other platforms and products, compatibility is equally important.Users must make sure that their current hubs or controllers support the Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or Z-Wave protocols used by the majority of smart home devices. Additionally, because it allows users to control multiple devices with a single interface or voice commands, compatibility with well-known voice assistants like Apple HomeKit, Google Assistant, and Amazon Alexa is frequently a deciding factor. Incompatibility can result in disjointed systems that are challenging to maintain or necessitate the use of multiple apps, which lowers user satisfaction and convenience. Before making a purchase, some manufacturers assist customers in determining whether their devices will work together by offering comprehensive compatibility lists or online resources. Firmware updates and software support also guarantee that devices remain compatible over time and continue to perform well in the face of evolving technological standards. Even though a lot of modern devices are designed to be do-it-yourself (DIY) friendly, complex setups or situations involving electrical wiring may occasionally call for professional installation. All things considered, widespread compatibility and ease of installation are essential to making smart technology accessible, usable, and enjoyable for everyday people.