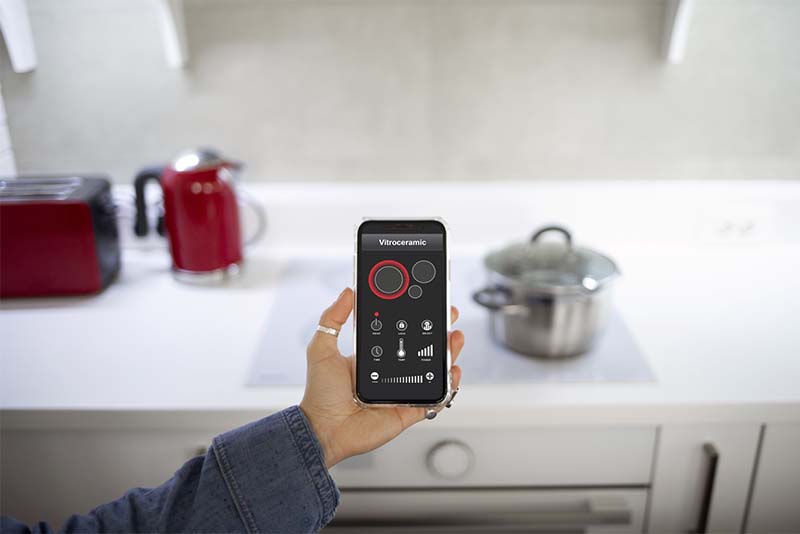
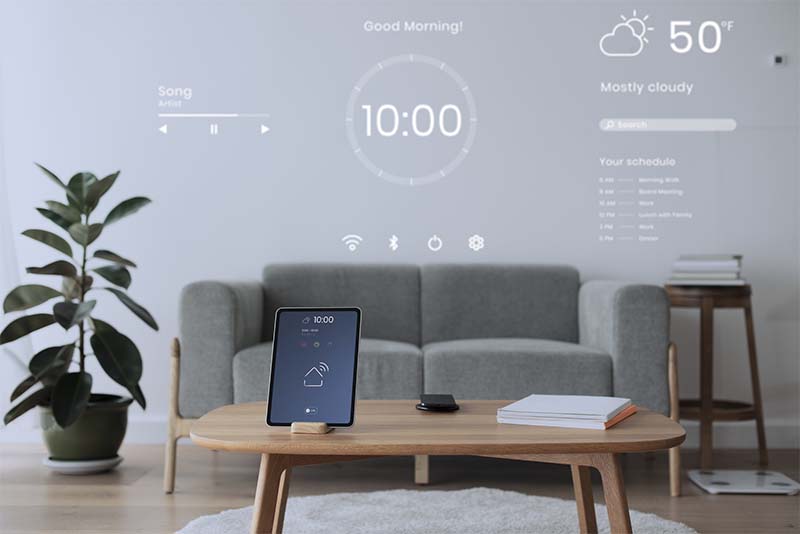
Smart control is a characterizing aspect of contemporary smart devices, including lighting, thermostats, appliances, and home energy monitors. They can be remotely, intelligently controlled, automated, and monitored using digital interfaces such as voice assistants, smartphone apps, or central smart home hubs. Conventional devices are transformed into flexible, interactive components of a networked home with this level of control.
Essentially, smart control allows one to monitor and control devices remotely from anywhere there is an internet connection. Homeowners can even access real-time monitoring of their energy usage, change the thermostat setting, and switch lights on and off even while away from home using a smartphone app. With real-time management, remote control brings comfort, convenience, and more energy efficiency.
Beyond simple on/off operations, smart control often involves advanced automation. By switching off lights at night or reducing temperature while someone is out, gadgets can be made to learn automatically about their daily schedules. Some systems dynamically adapt in accordance with sensors or patterns to ensure they are always comfortable and efficient without needing manual control.
By facilitating hands-free operation using apps such as Apple Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa, voice control bolsters smart control. This way, users can just ask, for instance, “What’s my current energy consumption?” or “Turn off the living room lights” and receive instant feedback and response.
Customization and personalization are other benefits. Users may create scenes or groups with smart control interfaces, which control multiple devices at a time for specific activities or atmospheres, such as a “movie night” mode that adjusts the temperature and lowers the lights. Alerts and notifications can also be customized to inform users about unusual activity, power spikes, or the requirement for maintenance in devices.
Smart control also adds security since it enables users to monitor and manage devices remotely, reducing the risk of leaving appliances on accidentally or utilizing simulated presence lighting to deter intruders.
In summary, smart control allows individuals to manage their home environment intelligently, practically, and adaptablely. It is more comfortable, efficient, secure, and sustainable because it makes daily devices more responsive, connected, and easy to use from almost anywhere.
- Voice Assistant Compatible
Voice assistant compatibility is an important feature of many smart home devices, including smart energy monitors, lighting systems, thermostats, and appliances. This compatibility allows users to control their devices using voice commands through popular virtual assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri. Integrating voice assistants into smart home ecosystems enhances convenience, accessibility, and hands-free control.
If a smart device is voice assistant compatible, one can just issue voice commands to control it without having to resort to a smartphone application or physical controls. One can say, for instance, “Alexa, turn off the living room lights,” or “Hey Google, show me my energy consumption today.” Such hands-free interaction is particularly convenient when multitasking, in the kitchen, or if one has mobility issues.
Voice assistant integration also enables more natural, conversational use. Most assistants respond to follow-up questions and context, so users can request detailed energy reports, manage multiple devices simultaneously, or create voice-controlled routines. For example, a “Goodnight” routine could turn off all of the lights, adjust the thermostat, and confirm whether or not any appliances remain on.
Pairing the smart device app to the voice platform using an account link or “skill” enablement is often required for integration with voice assistants. Devices can be organized into rooms or zones after they are paired, making more streamlined commands such as “Turn off all kitchen devices” possible. Multiple device management is simplified and powerful due to this organization.
Additionally, voice control improves accessibility for older people or users with disabilities who might find traditional controls difficult to use. It offers a straightforward and efficient method of interacting with technology, promoting self-reliance and enhancing quality of life.
Compatibility with voice assistants can save energy in addition to being convenient. Without interfering with their activities, users can quickly turn off devices that have been accidentally left on or change settings to maximize consumption.
In conclusion, voice assistant compatibility turns smart home appliances into interactive, voice-activated assistants. It makes smart homes easier to use and more integrated into everyday life by providing effortless control, customized routines, and enhanced accessibility.
- Adjustable Brightness and Color
Home lighting ambiance and functionality are greatly enhanced by the prominent features of most smart lighting devices, like smart LED bulbs, which are adjusted in terms of brightness as well as color. Apart from their functional benefits, the features allow users to change the color and brightness of their lights to suit different activities, moods, and parts of the day.
The light’s brightness can be changed by users. With bright, focused light for reading or working and soft, dim light for winding down or evening relaxation, this can help create the perfect atmosphere. Unlike traditional bulbs, which have limited brightness settings, smart lights offer smooth dimming from 1% to 100%. This makes precise control possible through mobile apps, remote controls, or voice commands.
By allowing users to choose from any of the millions of RGB colors, color adjustment goes beyond customization. You can use the feature to enhance specific activities, coordinate the decor, or set the mood. For example, warm amber hues create a cozy atmosphere in the evening, while cool white light improves focus on tasks during the day. Red and green for Christmas or dynamic color shifting for parties are examples of celebratory occasions where colored lighting can be used.
Tunable color and brightness complement each other to offer benefits beyond cosmetics. Studies have shown that lighting quality influences humans’ productivity, mood, and well-being. Natural circadian cycles can be complemented with dynamic white light that also shifts in color temperature with the passage of time, helping users feel more alert during the day and more refreshed at night.
These types of smart lighting frequently interface with voice assistants and smart home systems, enabling smooth automation or voice control. Scenes or schedules that automatically change color and brightness according to time or activity can be programmed by users; for instance, warm, dimmer light at night and bright daylight tones in the morning.
In summary, adjustable brightness and color give users unparalleled flexibility in lighting their spaces. This capability enhances comfort, wellness, and personal expression, transforming lighting from a simple utility into a dynamic and interactive experience tailored to individual needs and preferences.
In order to give users automated control over when their devices turn on or off, scheduling and timers are essential components of smart home appliances, particularly energy management and smart lighting systems. These tools provide convenience, energy savings, and improved home security by allowing users to program their devices to run for specified periods of time.
By using scheduling, users can program devices to carry out weekly or daily tasks automatically and without human intervention. For instance, a homeowner might program outdoor lights to turn on at night or bed lights to turn on at sunset and turn off at bedtime. Automation through scheduling improves lifestyle comfort and convenience by delivering consistent lighting behavior based on environmental factors or personal routines.
Timers give devices flexibility by allowing them to operate for a predetermined amount of time before automatically shutting down. To save energy if someone forgets to manually turn off a bathroom fan or light, they could program a timer to do so after 15 or 30 minutes.
These features, which are typically accessible through mobile applications, make it simple for users to create, modify, and oversee timers and schedules. Typically, the interfaces allow you to define multiple schedules for different rooms or units, or to set different settings for the week and the weekend.
By keeping devices turned off when not in use, timers and scheduling also conserve energy. The cost of utility bills is reduced due to less electricity waste. Systematic energy savings can be accomplished, for example, by installing lights to turn off automatically while the house is unoccupied or by scheduling heating and cooling systems to be used only when the house is being occupied.
Scheduling and timers enhance home security in addition to convenience and cost savings. When residents are not home, automated lighting can create the illusion of occupancy, which discourages would-be burglars.
Users can set or modify schedules and timers with simple voice commands thanks to integration with voice assistants like Google Assistant and Alexa, which further improves usability.
In summary, scheduling and timers transform smart home devices into intelligent, self-managing tools that optimize convenience, save energy, and enhance security, all while adapting seamlessly to the user’s lifestyle and preferences.
Using less energy to accomplish the same task or achieve the same result is known as energy efficiency. Energy efficiency in the context of smart home appliances, lighting, and devices refers to the design and operation of products that use the least amount of electricity while still offering excellent performance and functionality.
Reduced electricity use, lower utility costs, and less environmental impact are all made possible by smart energy-efficient devices. For instance, LED lights are far more energy efficient than conventional incandescent bulbs; they can save up to 80% on electricity consumption and have a longer lifespan, which lowers waste and replacement expenses.
Another component of energy efficiency in smart homes is intelligent energy management. Examples of gadgets that optimize energy use by adapting to user behavior and environmental conditions include energy monitors and smart thermostats. For example, a smart thermostat learns your schedule and adjusts the heating or cooling to save energy when no one is home.
Features like motion detection, adaptive brightness, and auto shut-off are common in smart devices and help cut down on energy waste. Phantom loads, which cause a startling amount of energy waste in ordinary homes, can be addressed by smart plugs and power strips that can cut off power to appliances in standby mode.
The coordination of energy use throughout the system is just as important to energy efficiency as the performance of individual devices. Multiple devices can be coordinated by smart home hubs to operate in a way that balances comfort and low energy use. For example, window shades, HVAC, and lighting can all cooperate to maximize indoor lighting and temperature while using the least amount of energy.
Additionally, energy-efficient smart devices maximize clean energy use and decrease grid dependency by coordinating energy use with peak generation times, supporting the integration of renewable energy sources like solar power systems.
In conclusion, energy-efficient smart home technology not only improves comfort but also helps you save money and preserve the environment. By reducing wasteful energy use and promoting more intelligent usage patterns, these gadgets are essential to sustainable living and the battle against climate change.
One significant development in smart home technology is the “No Hub Required” feature, which makes setup easier, lowers expenses, and improves user convenience. Historically, in order to connect to a home network and facilitate communication between devices and apps, a specialized central hub or bridge was required for many smart devices, including sensors, plugs, and smart lights. In addition to requiring additional hardware and occasionally complicated installation, a hub serves as a central controller and is frequently connected via Zigbee, Z-Wave, or other protocols.
Users can now connect devices directly to their home Wi-Fi network thanks to the proliferation of smart devices that are Wi-Fi enabled and don’t need a hub. By doing away with the need for additional equipment, this direct connection lowers upfront costs and clutter. Users only need to download the app, connect the device to Wi-Fi, and start controlling it right away, eliminating the need to manage multiple pieces of hardware.
Among the many benefits of no-hub smart devices are scalability and ease of installation. Technical expertise, such as knowledge of device pairing and network protocols, is frequently needed to set up a hub-based system. On the other hand, no-hub devices usually include simple, easy-to-use apps that walk users through quick setup procedures, opening up smart home technology to a wider audience.
Flexibility is an additional benefit. Users can mix and match Wi-Fi-capable devices from various manufacturers to create a customized smart home ecosystem without a hub restricting the system to a specific brand or protocol. This interoperability avoids vendor lock-in and expands choice.
Some compromises exist, though. For hubless products, the reliability and strength of the Wi-Fi network are crucial. Patchy or weak Wi-Fi coverage will impact device functionality. Additionally, hubs provide more sophisticated features such as local processing and larger protocol support that may not be present on some Wi-Fi devices.
Despite these considerations, the no-hub approach aligns well with the trend towards simplicity and convenience in smart homes. It accelerates adoption by removing barriers to entry and making smart technology usable by virtually anyone with a smartphone and Wi-Fi.
In conclusion, “No Hub Required” devices offer an easy, affordable, and flexible way to create a smart home. They simplify installation, reduce complexity, and open smart living to a wider audience, fostering a more seamless and connected lifestyle.
In smart home ecosystems, group control is a potent feature that enables users to control several devices at once as a single entity. Group control allows users to arrange smart devices, like plugs, lights, and thermostats, into groups according to rooms, zones, or functions and control them all at once rather than controlling each one separately. This feature improves smart home customization, efficiency, and convenience.
Easy management is the primary advantage of group control. For example, users can define a “Living Room” group and switch off all the associated devices with one tap in the app or with a simple voice command, without the hassle of turning each light in the living room off individually. Especially in houses with many connected devices, this saves time and makes it easier to manage several smart devices.
In addition, group control allows for smoother and more interactive smart home experiences. By bundling multiple devices together and turning them on/off simultaneously, users are able to have scenes or atmospheres. For instance, in a “Movie Night” atmosphere, one command or tap may turn off the living room lights, close the smart curtains, and adjust the thermostat to a comfortable level.
Group control increases energy efficiency in addition to convenience. Group device management makes it simple for users to make sure that whole sections of the house are turned off when not in use, saving energy. For instance, it is easier and more dependable to turn off all of the lights and electronics in the bedroom at night than to control each one individually.
The majority of smart home applications offer user-friendly interfaces for group creation and customization. Users have the ability to rename groups, add or remove devices, and give them schedules or automation rules. Group control is further improved by integration with voice assistants like Apple Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa, which enable voice commands like “Turn off all the lights upstairs.”
In larger homes or multi-zone settings, where controlling individual devices can become daunting, group control is extremely helpful. By lowering the number of interactions required to manage the home environment, it also promotes accessibility.
In summary, group control brings simplicity, efficiency, and enhanced user experience to smart homes by enabling centralized operation of multiple devices. It empowers users to effortlessly customize, automate, and optimize their connected environments with ease.
In order to improve security and energy efficiency when residents are not home, many smart home devices have the popular feature known as “Away Mode.” Away Mode gives homeowners peace of mind while they are away by reducing needless energy use and discouraging possible intruders by simulating occupancy.
Away Mode’s main concept is to simulate normal daily activities to give the impression that someone is still at home. This is a common use for smart lighting, which simulates natural household activity by turning lights on and off at different times. Home security is increased by this randomization, which makes it more difficult for outsiders to predict the pattern.
Before you leave the house, simply use a voice command or a smartphone app to put the device into Away Mode. After being turned on, the system either adheres to a predetermined timetable or intelligently modifies itself based on past user behavior. To give the appearance of occupants, lights in the living room and porch, for instance, could be turned on in the evening and off late at night.
Some smart appliances and thermostats use Away Mode in addition to lighting to maximize energy efficiency. In order to save energy, heating or cooling systems may lower output without compromising comfort when they return. In order to avoid unnecessary standby power consumption, smart plugs can also be configured to switch off non-essential devices.
Away Mode frequently functions in tandem with other security features like cameras, motion detectors, and alarms. To deter intruders, the system can simulate additional activity, like turning on more lights or sounding an alarm, or it can trigger alerts if motion is detected unexpectedly.
By enabling Away Mode remotely, users can conveniently manage their home environment from any location, guaranteeing efficiency and security even during unplanned absences. Those with erratic schedules, frequent travelers, and vacationers will find it especially helpful.
In summary, Away Mode enhances smart home security by creating the illusion of occupancy, reducing the risk of break-ins. It also supports energy savings by managing devices efficiently while the home is empty. This feature provides a smart, automated way to protect and optimize the home environment whenever residents are away.
One of the central elements of intelligent home devices is simple setup, which simplifies the installation and setup process for devices so that users of all skill levels can easily install and setup the devices. Companies are focusing on making smart technology more accessible as it gains widespread use so that anyone, from technology novices to experts, can easily and quickly add intelligent devices to their residences.
The hallmark of an easy setup process is clear, detailed instructions, often delivered through intuitive mobile applications. These applications typically walk users through pairing devices with smartphones, connecting devices to Wi-Fi networks, and modifying basic settings with the help of concise instructions and useful illustrations. As a result, no additional hardware or specialized knowledge is required.
One key aspect of a simple setup is the plug-and-play functionality. Once you power it on and connect to your home network, many smart devices are ready to go right out of the box. This kind of immediate readiness speeds up the installation process and reduces frustration, making it easier for more people to embrace smart home technology.
By doing away with complicated wiring or hubs, wireless connectivity—especially Wi-Fi—plays a significant part in making setup simpler. Direct connections to pre-existing Wi-Fi networks enable more placement flexibility and eliminate the need for extra equipment, which lowers setup time and costs.
By allowing voice commands during setup or control, voice assistant integration further improves usability. For instance, a user can avoid more difficult manual procedures by using a few basic voice commands to integrate a smart light into an Alexa or Google Home ecosystem.
In order to assist users in identifying and resolving connectivity or configuration issues without professional assistance, troubleshooting is frequently integrated into the setup process through diagnostic tools or app notifications.
To help consumers who run into problems, many manufacturers provide a multitude of online resources, such as videos, frequently asked questions, and customer support.
In summary, easy setup transforms the smart home experience by making it accessible, convenient, and stress-free. By streamlining installation and configuration, it removes barriers to entry and empowers more people to enjoy the benefits of connected living quickly and confidently.
One of the main reasons why smart home technology is becoming so popular is affordability. Smart devices give homeowners the chance to improve comfort, security, and energy efficiency without going over budget as they become more widely available and competitively priced. Users from a wide range of financial backgrounds can take part in the connected home revolution thanks to reasonably priced smart devices.
The affordability of smart home appliances is largely due to mass production and technological advancements. Manufacturers are now able to produce high-quality products at more reasonable prices thanks to the decline in the price of components like Wi-Fi chips, sensors, and LEDs. Because it provides a variety of smart devices at prices that suit different budgets, consumers benefit from this trend.
Affordable smart devices frequently have dependable performance and easy-to-use features, demonstrating that high quality does not always need to be expensive. For example, smart plugs, bulbs, and energy monitors that fall into the mainstream price ranges still provide great value by having necessary features like scheduling, remote control, and energy monitoring.
The accessibility of reasonably priced smart devices promotes small, gradual improvements as opposed to significant upfront expenditures. Over time, homeowners can progressively grow their smart home ecosystem by starting with a single gadget, like a smart lightbulb or plug. This adaptability lowers the cost and increases accessibility to smart technology.
Additionally, low-cost smart home technology encourages energy conservation that can swiftly pay for itself. Users save money on utility bills by automating devices, cutting waste, and optimizing energy usage, which makes the investment financially sound in the long run.
In order to further improve affordability, retailers and online platforms frequently offer discounts, bundles, or starter kits. These bundles promote wider adoption by enabling customers to buy several devices at a discounted price.
However, compatibility and security are not sacrificed for affordability. To guarantee that users have a safe and connected experience, many low-cost devices continue to support crucial features like voice assistant compatibility, app integration, and encryption.
In summary, affordability plays a crucial role in democratizing smart home technology. By making smart devices accessible and cost-effective, it empowers more people to improve their homes’ comfort, convenience, and sustainability, fostering a smarter, more connected lifestyle for all.